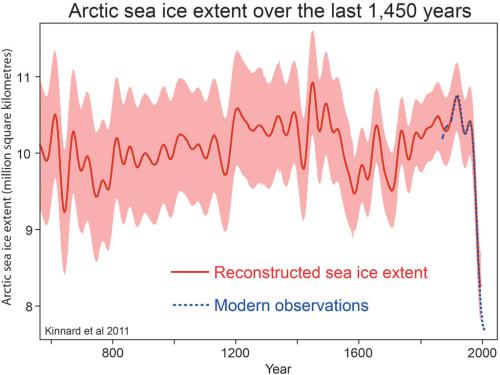
A new paper in Science (Kinnard et al 2011) reports that the recent loss in arctic sea ice is likely to be unique over the last 15 centuries and caused by greenhouse gas emissions.
Here we use a network of high-resolution terrestrial proxies from the circum-Arctic region to reconstruct past extents of summer sea ice, and show that—although extensive uncertainties remain, especially before the sixteenth century—both the duration and magnitude of the current decline in sea ice seem to be unprecedented for the past 1,450 years. Enhanced advection of warm Atlantic water to the Arctic seems to be the main factor driving the decline of sea ice extent on multidecadal timescales, and may result from nonlinear feedbacks between sea ice and the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation. These results reinforce the assertion that sea ice is an active component of Arctic climate variability and that the recent decrease in summer Arctic sea ice is consistent with anthropogenically forced warming.
Read a great summary post by Rob Painting at SkS.
Leave a Reply